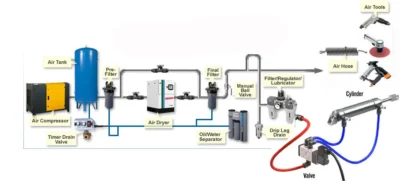
Pneumatic systems play a crucial role across a broad spectrum of industries and applications, ranging from air compressors to power tools and air brakes. These systems are so ubiquitous that many people use them without realizing it. But how exactly do pneumatic systems function?
What Is a Pneumatic System?
A pneumatic system operates by utilizing compressed air or gas to move and control mechanical components. These systems are employed in various fields, including manufacturing, automation, transportation, and construction.
At the heart of a pneumatic system are several key components:
- Storage tank: Holds the compressed air or gas.
- Compressor: Generates the compressed air or gas.
- Pneumatic components: Valves, cylinders, and actuators manage the air flow and pressure, transforming it into mechanical motion.
Pneumatics are often favored when electrical or hydraulic systems are impractical. They tend to be more affordable, easier to maintain, and can deliver precision and consistent operation, which is crucial in many applications.
How Do Pneumatic Systems Work?
The system starts by releasing compressed air from the storage tank. This air travels through a network of pipes to the pneumatic components. Valves regulate the air flow, while pressure regulators adjust the force, ensuring the system operates as needed.
Mechanical movement is created when the pneumatic components harness the energy of the compressed air. For instance, a pneumatic cylinder uses air pressure to push a piston, which then generates movement.
Advantages of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems offer numerous benefits, making them a go-to choice in many industries:
- Reliability: These systems are known for their robustness, resisting temperature changes, shock, and vibration. This makes them suitable for harsh environments, such as construction sites.
- Safety: Pneumatics are safe to use in hazardous conditions since they do not produce heat or sparks, reducing the risk of fire or explosions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They are generally more affordable compared to other systems, requiring fewer parts, being easier to install, and having longer lifespans with minimal maintenance.
- Flexibility: Pneumatic systems can be tailored to meet specific needs, working effectively in confined spaces or unique applications.
- Efficiency: With precise and consistent operation, pneumatic systems can power multiple components simultaneously, reducing the need for additional energy sources—a key benefit in remote environments.
Industries and Applications of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems are indispensable in various industries. Some common applications include:
- Manufacturing: Used for material handling, packaging, and assembly processes.
- Automotive: Found in braking, suspension, and transmission systems; air brakes on buses are a typical example.
- Aerospace: Pneumatics power braking systems and landing gear in aircraft.
- Food & Beverage: Used for conveying, filling, and packaging in food production.
- Medical & Pharmaceutical: Critical equipment such as ventilators, blood pressure monitors, and dental tools rely on pneumatic systems.
- Construction: Pneumatics power tools and machinery on construction sites, particularly where electrical power sources are unavailable.
From improving safety to reducing operational costs, pneumatic systems remain a vital technology across many industries, providing reliable, efficient solutions for various mechanical needs.



